How to receive medical care
(Information on medical institutions)
Procedures and precautions in accepting medical tourists
Flow from an inquiry to a decision of acceptance
- ●In-hospital coordination of acceptance judgment
-
- - The hospital staff obtains information about the inquiry and medical information from the patient or international medical coordination operator, conveys patient information to the physician in charge, and determines whether to accept the patient.
- - After in-hospital coordination, the hospital staff conveys the decision of acceptance or rejection to the patient or international medical coordination operator.
- ●When the patient is accepted
-
- - The hospital staff conveys details of the treatment and hospitalization duration to the medical administration personnel, prepares an approximate estimate of treatment, and conveys it to the patient or international medical coordination operator.
- - The hospital staff communicates with the patient on the period the patient can stay in Japan and his/her request for hospitalization and treatment and reserves examination appointments and a bed required for the hospitalization period and examination items.

Preparation and procedure before arrival in Japan
- ●Preparation and sending of documents necessary for issuance of visa for medical stay
-
- - When patients living in overseas countries visit Japan to seek medical care, they must obtain a “visa for medical stay.”
- - The Hospital Director or primary physician of the patient confirms the documents for issuance of visa for medical stay and sends them to the registered guarantor.
- ●Preparation of the Informed Consent Form
-
- - Informed Consent Forms necessary for hospitalization and treatment are sent to the international medical coordination operator.
- ●Preparation for medical fee payment
-
- - Acceptance of foreign patients is associated with a risk of accounts receivable of the medical fee. Medical institutions therefore must take measures against accounts receivable by requesting patients to pay for treatment in advance or pay via the deposit system.
- - The hospital prepares invoices based on the determined treatment and schedule and requests hospitalization for the patient or via the international medical coordination operator.

In-hospital coordination during stay in Japan
- ●Coordination for hospitalization, treatment, and examinations
-
- - The section in charge of consultation shall be designated in advance to be prepared for cases where patients and accompanying persons have problems during the hospital stay or where the medical staff wants to confirm or consult on the policies of examinations and treatment.
- - For example, the contact person shall always be available, and ward nurses and ward clerks shall take initiative in guiding of patients, coordination between primary physicians and examination staff, and clerical procedures so that the medical staff can concentrate on treatment and examinations.

Point!
Designation of the section in charge and coordinator in charge of patient acceptance

●Medical coordinator in accepting foreign patients: Person in charge of duties necessary for acceptance in the hospital
- (1) The medical coordinator supports communication with patients and their families, makes interdepartmental and interdisciplinary coordination in the hospital, promotes cooperation and coordination with outside organizations, and collects information in and outside the hospital to improve the system.
- (2) A dedicated coordinator may be appointed or several sections or persons may share the coordination function to establish a system appropriate for each hospital.
- (3) Staff assignment is determined based on three staffing models by taking into consideration the “number of patients accepted” and “types of coordination functions”: 1) Dedicated coordinator assignment model, 2) role-concurrent coordinator assignment model, and 3) role sharing model.
Model diagram of personnel allocation for medical coordination functions in accepting international patients
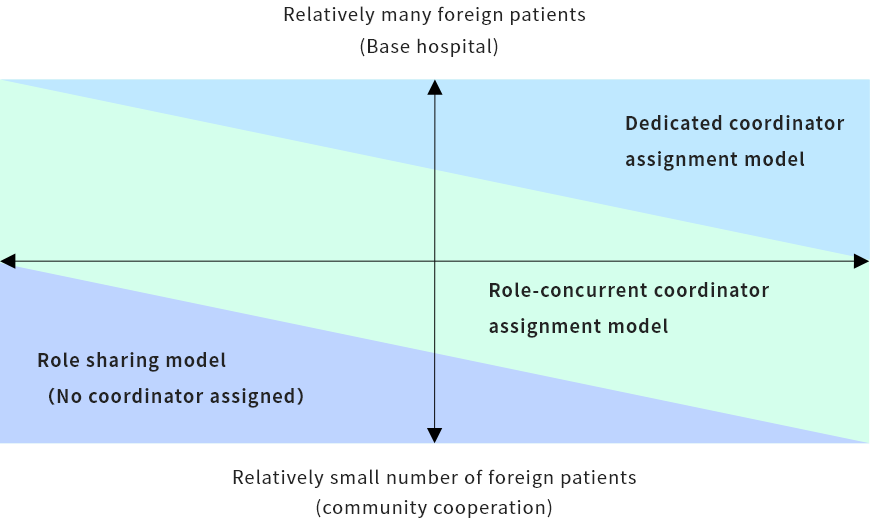
- Work allocation
- Example: The coordinator educates the hospital staff on usage of the medical translation tool and response flow as a part of system improvement, and the on-site staff members take charge of care of patients in principle.
- Work centralization
- Example: The coordinator (person in charge) alone understands usage of the medical translation tool and attends to foreign patients in principle. (The on-site staff members take care of them in a similar manner to Japanese patients.)
Reference: Curriculum textbook of "Medical Coordinator Development Training for Accepting Foreign Patients," a project commissioned by the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (Feb. 2020)
Source: "Aichi's Medical Tourism ~Toward acceptance of foreign patients visiting Japan for medical care~ Advanced Level," Aichi Prefecture
Response in each scenario after acceptance
Reception
It is essential to know a language that the patient can use and to explain the rules of the hospital and details of the treatment to them carefully.
- - Ask each patient to fill out the Patient Registration Form to share recognition among staff members.
- - Confirm who can serve as an interpreter.
- - Copy the Residence Card, passport, and visa.
- - Ask the patient to fill out the Patient Registration Form and Interview Sheet, and start the medical care.
- ■Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare “List of medical institution search results”
- https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/kenkou_iryou/iryou/kokusai/setsumei-ml.html

Prior explanation to those who want to apply for medical tourism by the international medical coordination operator

Specific medical care is explained by physicians or other healthcare professionals of medical institutions that accept foreign patients. However, it is necessary to meticulously explain rules of Japanese medical institutions, what can or cannot be provided, and differences from patients’ home countries as a preliminary step.
- - Since there are cases in which foreign patients request healthcare not included in the original plan, causing confusion in the clinical setting, it is essential to convey precautions in advance, such as “patients cannot make requests on the day,” and make sure they understand them.
- Explanation of precautions unrelated to medical practices will impose a significant burden on medical institutions that accept foreign patients and may cause problems later if the content cannot be communicated precisely. Therefore, explanation of such precautions can be effectively provided by the international medical coordination operator.
Consideration for respective cultures, religions, and customs
- ●Confirmation of requests of and consideration in terms of religions and customs
-
- - Before starting examinations, consultation, and treatments, confirm any requests and considerations in terms of patients’ cultures, religions, and customs, and explain what kinds of requests cannot be fulfilled in advance. This approach will enhance patient satisfaction and avoid unexpected problems.
- ●Arrangement of hospital meals
-
- - There may be dietary restrictions due to religious doctrines and beliefs. Some patients may ask for a detailed explanation about ingredients and cooking procedures. It is good to prepare multilingual menus and photos to explain ingredients, cooking procedures, and finished meals.
[Major religions and their precepts and customs]
| Major religions | Religious precepts / Customs |
|---|---|
| Islam (Muslim religion) |
|
| Hinduism |
|
| Judaism |
|
| Buddhism |
|
| Christianity |
|
| Jainism (a religion in India) |
|
- Ingredients prohibited due to ideological reasons, such as animal rights and environmental preservation
“Lacto vegetarian”: Eat dairy products but do eat meat, seafood, and egg.
“Ovo vegetarian”: Eat dairy products and egg but do not eat meat and seafood.
“Vegan”: Do not eat all animal-source products (including meat, seafood, dairy products, and egg) and honey and do not use leather items and other animal-derived products.
Source: "Aichi's Medical Tourism~Toward acceptance of foreign patients visiting Japan for medical care~Advanced Level," Aichi Prefecture(Major religions and their precepts/customs)
Discharge and preparation of the medical certificate
- ●Preparation of post-discharge care plan
-
- - Establish a follow-up system such as by preparing a post-discharge care plan and medical records by the time of discharge so that patients can receive continuous treatment at a local medical institution after they go back home.
- ●Preparation and issuance procedure of the medical certificate
-
- - Check whether the medical certificate should be of the format designated by the patient or the hospital’s format.
- - Explain that the preparation and issuance procedure of the multilingual medical certificate will take a number of days, convey the fee and scheduled date of issuance, and collect the documentation fee.
- * This process will be smoothly performed with prior confirmation via the international medical coordination operator.
Countermeasures for accounts receivable

- ●Advance presentation of estimated medical expenses
-
- - It is important to admit patients after estimated medical expenses are presented to the patient in advance, the breakdown of the medical expenses, such as examinations and treatment, is explained, and the patients understand and agree with the expenses. This can prevent problems.
Reference: "Aichi's Medical Tourism~Toward acceptance of foreign patients visiting Japan for medical care~Advanced Level," Aichi Prefecture(Determination of unit price of medical care, measures against unpaid fees)
- ●Utilization of collection agency services
-
- - A risk of accounts receivable could occur, and medical institutions may hesitate to accept foreign patients. However, a collection agency service of the international medical coordination operator may be used. In this process, estimated medical expenses are conveyed to the international medical coordination operator, who in turn charges the expenses to patients by deposits or credit card payment.
- * When utilizing the international medical coordination operator, it is recommended that the medical institution, international medical coordination operator, and patient enter into an agreement on medical expense payment by the operator to the medical institution on behalf of the patient.
List of registered guarantors (International medical coordination operators)
From the link below, you can access the list of guarantors (international medical coordination operators) registered on the website of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
List of Registered Guarantors (Medical Coordinators etc.)
Download "Aichi's Medical Tourism"
This site provides useful information on accepting medical tourism, including basic processes for admitting foreign patients who speak different languages in performing medical tourism, so that medical institutions can maintain an environment that enables providing medical care to foreign patients safely and reliably and smoothly admitting them while ensuring the quality of medical care.

 Search medical institutions in Aichi.
Search medical institutions in Aichi.










